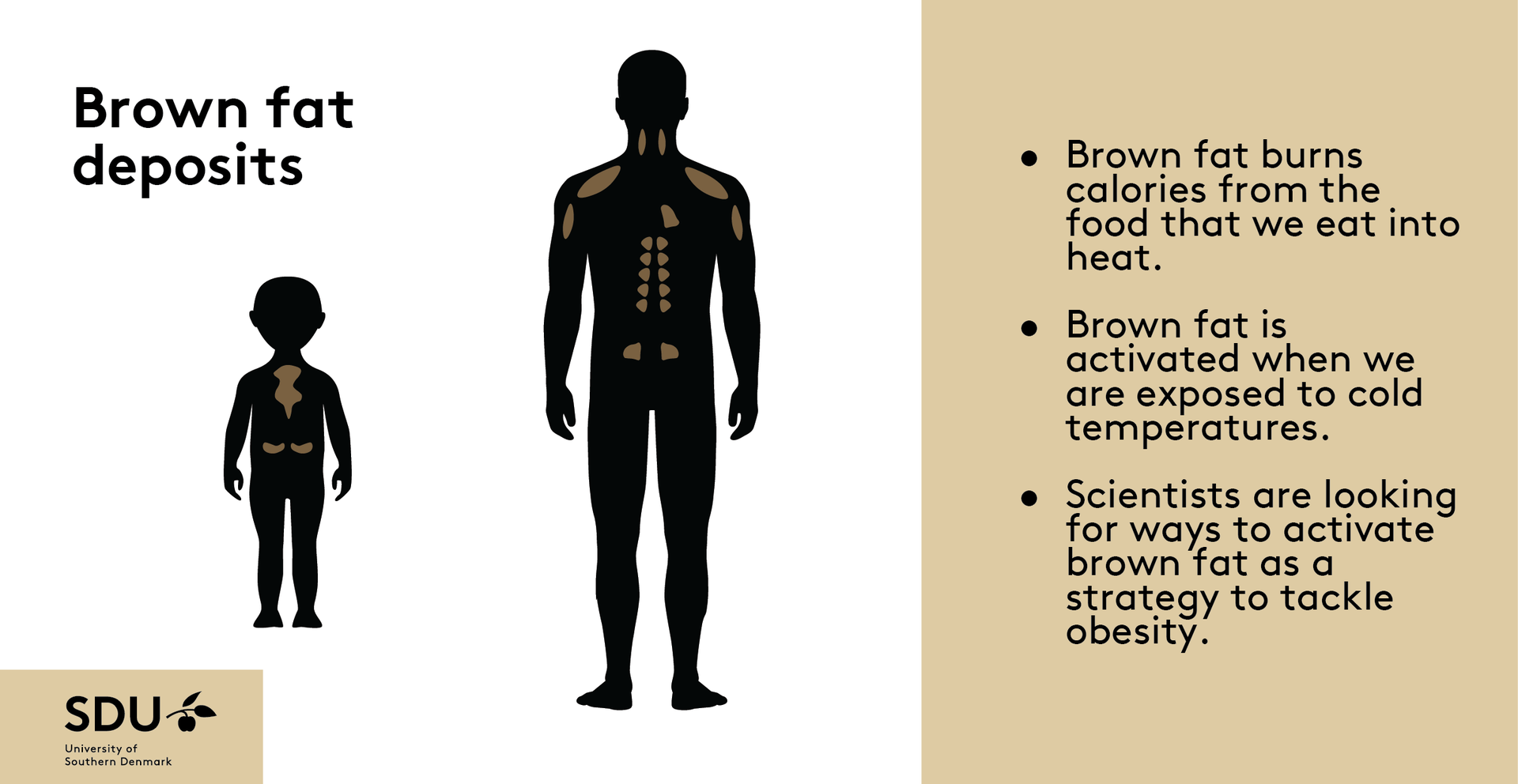
Brown fat, also known as brown adipose tissue (BAT), is a type of fat in our bodies that's different from the white fat around our belly and thighs that we are more familiar with. Brown fat has a special job—it helps to burn calories from the foods that we eat into heat, which can be helpful, especially when we're exposed to cold temperatures like during winter swimming or cryotherapy. For a long time, scientists thought that only small animals like mice and newborns had brown fat. But new research shows that a certain number of adults maintain their brown fat throughout life. Because brown fat is so good at burning calories, scientists are trying to find ways to activate it safely using drugs that boost its heat-producing abilities.
A new study from the research groups of Prof. Jan-Wilhelm Kornfeld from the University of Southern Denmark and the Novo Nordisk Center for Adipocyte Signaling and Dagmar Wachten from the University Hospital Bonn and the University of Bonn (Germany) has found that brown fat has a previously unknown built-in mechanism that switches it off shortly after being activated. This limits its effectiveness as treatment against obesity. According to first author of the study, Hande Topel, who is a Senior Postdoc at the University of Southern Denmark and the Novo Nordisk Center for Adipocyte Signaling (Adiposign), the team has now discovered a protein responsible for this switching-off process. It is called ‘AC3-AT’.
Blocking the "off switch" opens up a new strategy
“Looking ahead, we think that finding ways to block AC3-AT could be a promising strategy for safely activating brown fat and tackling obesity and related health problems”, Hande Topel says. The research team found the switch-off protein using advanced technology predicting unknown proteins. Hande Topel explains: “When we investigated mice that genetically didn't have AC3-AT, we found that they were protected from becoming obese, partly because their bodies were simply better at burning off calories and were able to increase their metabolic rates through activating brown fat”.
Two groups of mice were fed a high-fat diet for 15 weeks, which rendered them obese. The group that had their AC3-AT protein removed, gained less weight than the control group and were metabolically healthier. “The mice that have no AC3-AT protein, also accumulated less fat in their body and increased their lean mass when compared to the control mice”, says co-author, Ronja Kardinal, who is a PhD student at the University of Bonn in the lab of Dagmar Wachten at UKB, continuing: “As AC3-AT is found not only in mice but also in humans and other species, there are direct therapeutic implications for humans”.
Hope for strategies that support weight loss
Although the prevalence of brown fat decreases as humans age, and despite grown-ups not having as much brown fat as newborns, it can still be activated, for instance by cold exposure. When it gets activated, it enhances the rate of metabolism of these individuals, which again may help to stabilize weight loss in conditions where calorie intake is (too) high. Intriguingly, this study not only identified AC3-AT, which is a shorter, previously unknown form of the AC3protein. The researchers also identified other unknown protein/gene versions, that respond to cold exposure, similar to AC3-AT.
“However, further research is needed to elucidate the therapeutic impact of these alternative gene products and their regulatory mechanisms during BAT activation”, says co-corresponding author Prof. Dagmar Wachten, Co-Director of the Institute of Innate Immunity at the UKB and member of the Cluster of Excellence ImmunoSensation2 and the Transdisciplinary Research Areas (TRA) "Modelling" and "Life & Health" at the University of Bonn.
“Understanding these kinds of molecular mechanisms not only sheds light on the regulation of brown fat but also holds promise for unraveling similar mechanisms in other cellular pathways. This knowledge can be instrumental in advancing our understanding of various diseases and in the development of novel treatments”, says co-corresponding author Prof. Jan-Wilhelm Kornfeld, University of Southern Denmark.